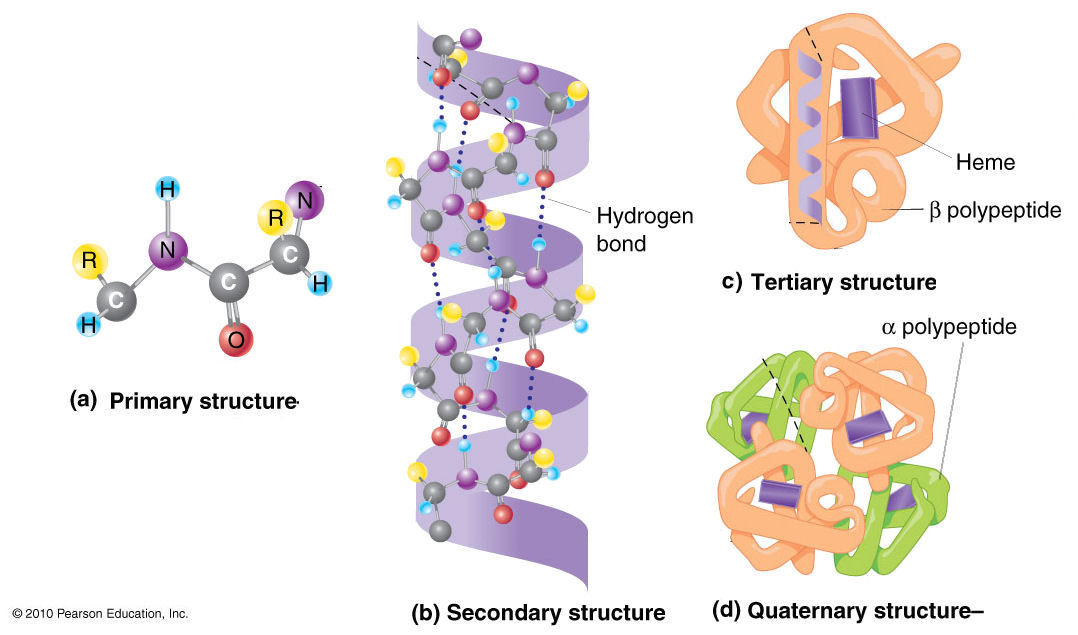
Describe the Differences in the Four Protein Structures.
Within our computational time one single simulation cannot cover a whole FEL containing all the important structures of S-protein. The leucine zipper contains four or five leucine residues spaced at intervals of seven amino acids resulting in their hydrophobic side chains being exposed at one side of a helical region.
Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry
The alpha helix is also called a classic PaulingCoreyBranson α-helixThe name 36 13-helix is also.
. The committee developed four core ideas reflecting unifying principles in life sciences. These core ideas are essential for a conceptual understanding of the life sciences and will enable students to make sense of emerging research findings. We train 10 different models with the same architecture on each of the trainingtest-set splits.
Although the genetic material in each of the cells is identical small differences in the immediate. Calponin is a smooth muscle-specific thin-filament protein with biochemical properties very similar to those of caldesmon. However the subcellular distribution of these two proteins differs in smooth muscle cells.
Using the structures selected after the initial filtering we carry out a k 10-fold cross-validation splitting the structures in training sets of 6860 structures and test sets of 762 structures approximately based on the scPDB clusters ie. The repeating or monomer units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are known as nucleotidesThe deoxyribonucleic acid DNA of a typical mammalian cell contains about 3 10 9 nucleotides. This region serves as the dimerization domain for the two protein subunits which are held together by hydrophobic interactions between the leucine side chains.
The total amounts of caldesmon are increased four- to fivefold in pregnant myometrium. Three-Up structures which were found with cryo-EM for instance PDB7DCC Zhang et al 2021b were not observed in the current simulations. Nucleotides can be further broken down to phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 a pentose sugar a sugar with five carbon atoms and a nitrogenous base a base.
As we discuss in the next section glycans on the surface of S-protein. The alpha helix α-helix is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone NH group hydrogen bonds to the backbone CO group of the amino acid located four residues earlier along the protein sequence.

Four Levels Of Protein Structure

Major Differences Com Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Protein Biology

Learn About The 4 Different Types Of Protein Structure Protein Biology Biochemistry Teaching Biology

No comments for "Describe the Differences in the Four Protein Structures."
Post a Comment